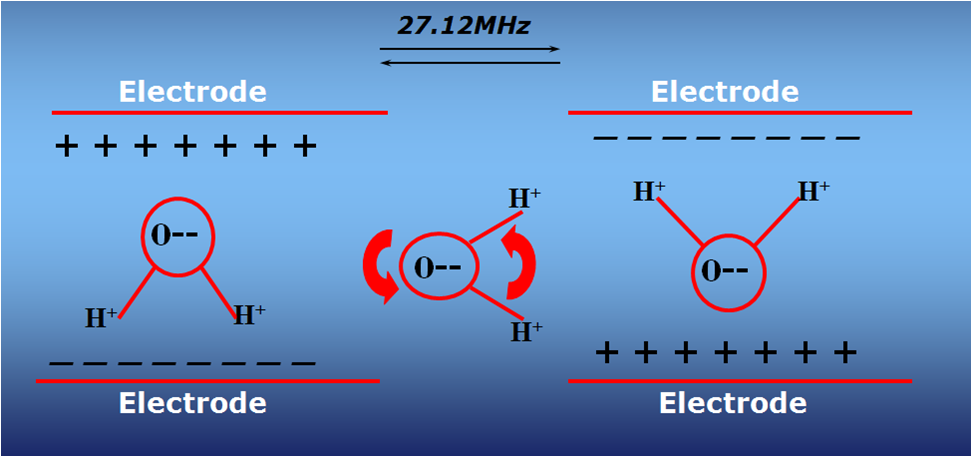
27.12MHz
RF Technology and Advantages
Radio Frequency Technology
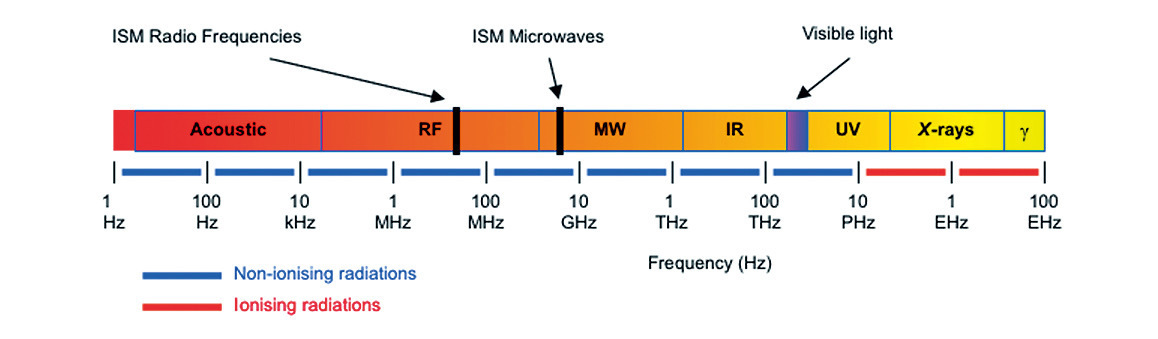
Electromagnetic wave:
Electromagnetic wave is formed by the combination and synchronous action of electricity and magnetic field, and its intensity changes with a certain oscillation frequency.

Due to the interaction of electromagnetic waves with matter (atoms, molecules, ions), heat can be directly generated in several materials under certain conditions. The heating mechanism depends on the frequency of the electromagnetic wave applied, as well as the specific chemical and physical properties of the material.
Since radio frequency is widely used by radio communication systems, in order to avoid interference, the competent authorities have allocated specific frequency ranges (bands) for industrial, scientific and medical purposes worldwide. The permitted frequencies in the RF range for dielectric heating applications are: 13.56, 27.12 and 40.68 MHz.
Dielectric heating:
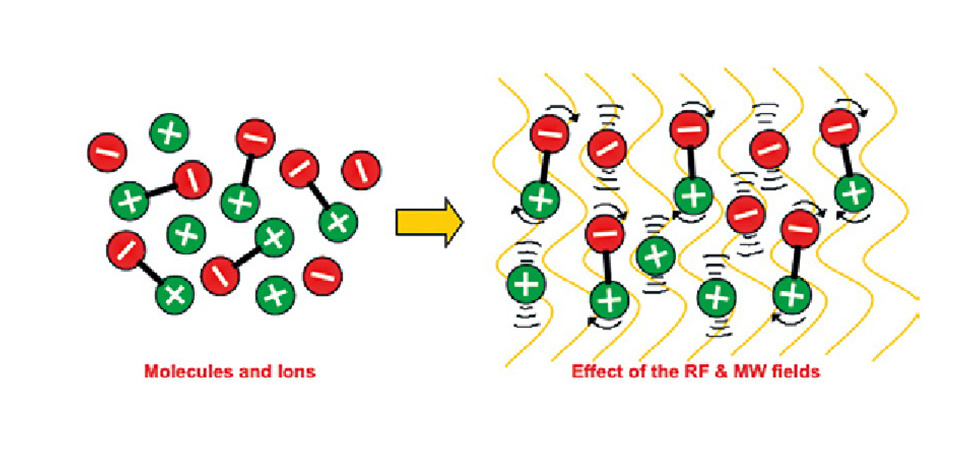
If we do not consider materials, especially good conductors of electric current: metals, for all other materials placed in the electromagnetic field, heat is mainly generated by what is called dielectric loss.
Dielectric loss is caused by the vibration and rotation of polar or polarized molecules, the polarization and translational motion of ionic particles represented in the material, and the rapid (tens of millions of polarity reversals per second) of the electromagnetic field.
This can be interpreted to mean that the electromagnetic field is absorbed and converted into heat energy due to the rapid movement of polar (polarized) molecules and ions. Water molecules are highly polar, more so than all common aqueous substrates, and many ions are usually dissolved in water. As a result, radiofrequency electromagnetic fields can rapidly heat substances containing water. In particular, RF can quickly, efficiently and selectively evaporate water from many substrates (textiles, agricultural products, bakery products, etc.).
Advantages of medium heating:
The radio frequency generates heat directly and instantaneously deep inside the product. Instead, traditional methods first generate heat outside the product and then transfer it through well-known heat conduction mechanisms (conduction, convection, radiation). Internal heat generation is the key to making RF heating fast, efficient and guaranteeing the best product quality, while eliminating all the typical disadvantages of traditional methods (slow heating, surface overheating, heat loss, etc.).
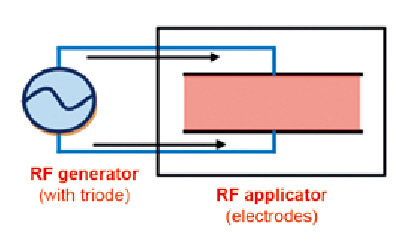
Typical structure of RF heating equipment:
In general, all RF heating equipment consists of two main parts:
- The generator
- Applicator (or electrode)
The generator converts the mains power from the main source to radio-frequency electromagnetic energy. It consists of a well-designed combination of capacitors and inductors (oscillating circuits) connected to a vacuum valve (vacuum tube) and equipped with a high voltage DC power supply. The applicator receives electromagnetic energy from the generator via a simple conductive metal connector and applies it to the heated product.

No. 98, Lane 4788, Bao 'an Highway, Anting Town, Jiading District, Shanghai
Copyright of the page: Shanghai Deyi Machinery Manufacturing Co., Ltd www.300.cn SEO Privacy Policy
